Results of a recent study that analyzed high-resolution images captured with a custom optical coherence tomography (OCT) device demonstrate that the concentration of pilocarpine in presbyopia-correcting eyedrops has a meaningful impact on their mechanism of action.1
For the study, anterior-segment OCT imaging was performed at baseline and 1 hour after instillation of balanced salt solution (BSS, control), pilocarpine 0.4% (Qlosi, Orasis), and pilocarpine 2.0% under accommodative stimuli of 0 D and 2.50 D. The prospective, single-center study enrolled 10 patients (mean age 51.5 years, range 46.3 to 63.4) with spherical equivalent of -2.50 D to +2.00 D. All 10 patients received all three products, spread over weeks.
The results showed that pilocarpine behaves in a concentration-dependent manner on the ciliary muscle during accommodation. Qlosi, low-concentration (0.4%) pilocarpine, demonstrated no statistically significant change in ciliary muscle movement at near, unlike high concentration (2%) pilocarpine, which demonstrated a significant change (Figure 1).
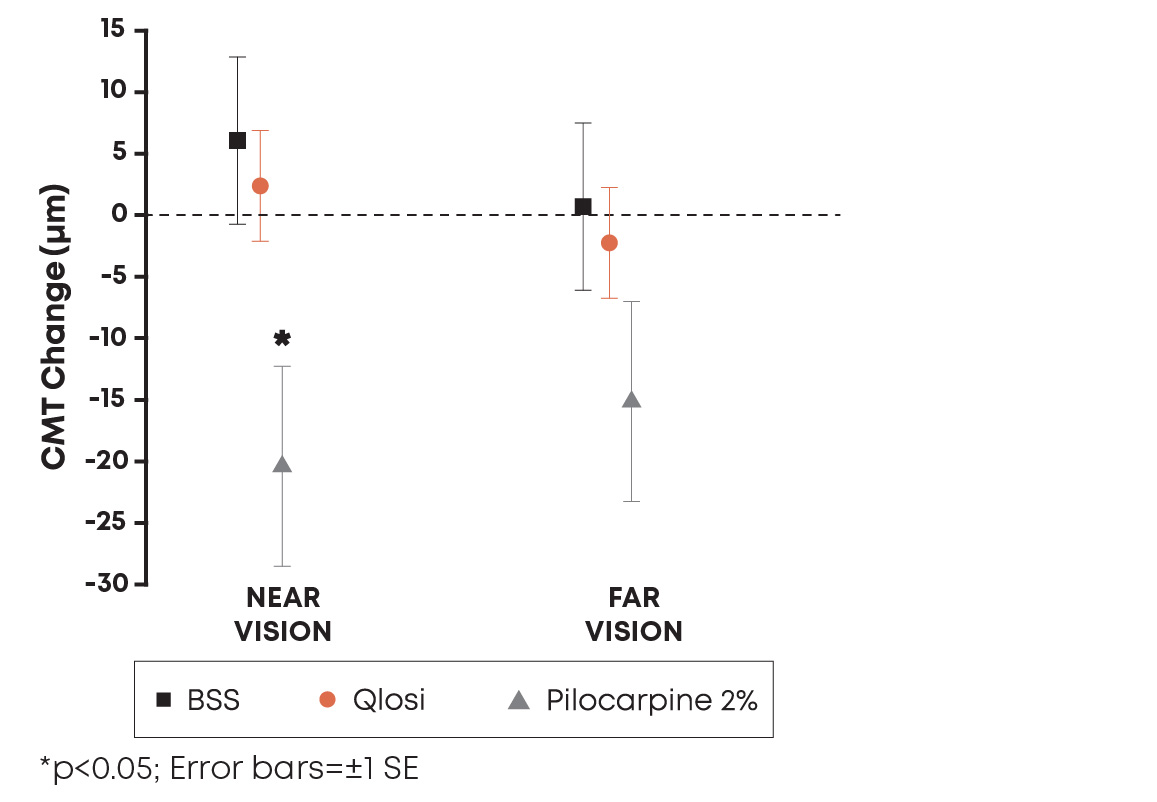
Figure 1. Pilocarpine behaved in a concentration-dependent manner on the ciliary muscle. Abbreviations: BSS, balanced salt solution; CMT, ciliary muscle thickness; µm, micrometer; SE, standard error.
Pilocarpine 2% showed a statistically significant change in ciliary muscle movement not observed in the BSS or pilocarpine 0.4% groups. These findings demonstrate that pilocarpine behaves in a concentration-dependent manner with regard to ciliary muscle movement, reinforcing the concept that formulation truly matters.
Qlosi (pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution) 0.4% is a cholinergic receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of presbyopia in adults. The formulation gained FDA approval based on results from the NEAR-1 and NEAR-2 phase 3 clinical trials. In the phase 3 studies, which enrolled 613 patients (Qlosi = 309, vehicle = 304), two doses were instilled in each eye for 2 weeks, and assessments were performed on day 1, 8, and 15. The study met its primary endpoint in demonstrating that 40% of presbyopic patients on Qlosi achieved a ≥3-line improvement in monocular distance-corrected near visual acuity (DCNVA), with no loss of 1 line or more in distance visual acuity, on day 8 at 1 hour post-dose 1 versus those receiving the vehicle (19%) (P <.0001).2 In a post hoc analysis, functional near vision was extended for up to 8 hours after two doses of Qlosi (Figure 2).

Figure 2. In the NEAR-1 and NEAR-2 studies, functional near vision was extended for up to 8 hours in ~8/10 patients after two doses of Qlosi. Abbreviation: DCNVA, distance-corrected near visual acuity.
Qlosi demonstrated a favorable safety profile in the NEAR-1 and NEAR-2 studies. The most common non-ocular treatment-related adverse event (TEAE) was headache (6.8% Qlosi vs 0.7% vehicle). As for ocular TEAEs, the most commonly reported event was instillation site pain (5.8% Qlosi vs 0.3% vehicle). To date (9 months post-launch), Qlosi has not had any serious adverse events reported to the FDA FAERS reporting site. The importance of a peripheral retinal examination remains paramount to rule out existing retinal pathology before prescribing any miotic agents.
"In our head-to-head clinical study, pilocarpine 0.4% showed ciliary muscle movement comparable to control, BSS, while high concentration pilocarpine 2% showed ciliary muscle movement. These findings are very encouraging, supporting that pilocarpine 0.4% behaves in a concentration-dependent manner compared to a high-concentration miotic. The results reinforce that formulation truly matters and low-concentration options may be particularly meaningful for patients considering a presbyopia therapy,” said Florence Cabot, MD, Assistant Professor of Clinical Ophthalmology, Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Miami, FL. "
1. Manns F, Cabot F, Ruggeri M. ORASIS-Bascom Palmer Eye Institute Study: Effect of pilocarpine eye drops on ciliary muscle accommodative response; revised analysis by Gerard Smits. Presented at Hawaiian Eye & Retina 2026; January 17-23, 2026; Waikoloa Village, HI.
2. Holland E, Karpecki P, Fingeret M, et al. Efficacy and safety of CSF-1 (0.4% pilocarpine hydrochloride) in presbyopia: pooled results of the NEAR phase 3 randomized, clinical trials. Clin Ther. 2024;46(2):104-113.
Important Safety Information
INDICATION
QLOSI is indicated for the treatment of presbyopia in adults
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Advise patients to not drive or operate machinery if vision is not clear (e.g., blurred vision). Exercise caution in night driving and other hazardous occupations in poor illumination. Rare cases of retinal detachment have been reported with miotics. Examination of the retina is advised in all patients prior to initiation of therapy. Advise patients to seek immediate medical care with sudden onset of flashes of lights, floaters, or vision loss.
QLOSI is not recommended to be used when iritis is present.
QLOSI should not be administered while wearing contact lenses. Remove lenses prior to the instillation of QLOSI and wait 10 minutes before reinsertion.
Avoid touching the tip of the vial to the eye or any other surface.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (5% to 8%) are instillation site pain and headaches.
QLO.00501


