I developed the rotary chop technique for two main reasons: (1) to tackle dense cataracts and (2) to teach trainees how to chop nuclei. I wanted to create an option for phaco-only surgeons that can improve safety and reduce cumulative dissipated energy. Chopping techniques are difficult for trainees to master, and I have found that my method can shorten the learning curve. By preplacing holes, the surgeon moves the chopper deep inside a dense cataract, enabling much easier chopping than if a standard vertical or horizontal chopping technique is used.
THE TECHNIQUE
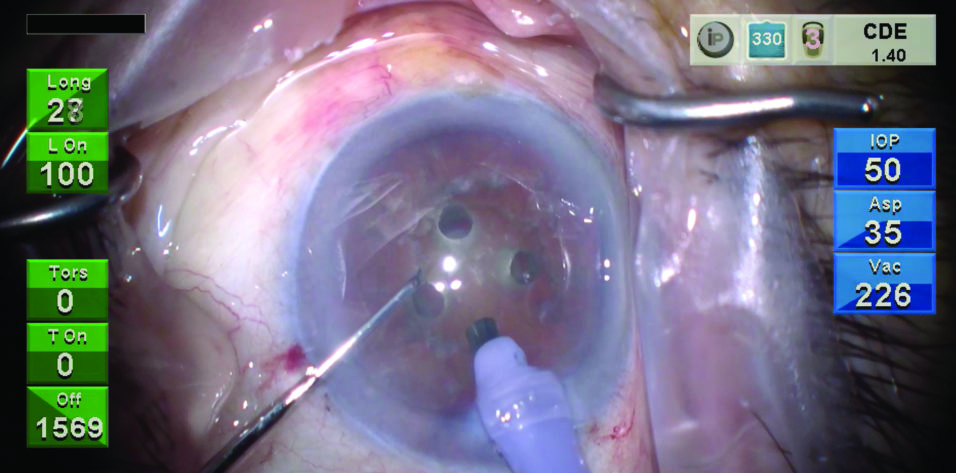
I coined the term rotary chop because the pilot holes created in the nucleus of the cataract resemble those on a rotary phone and because nuclear rotation is an important part of the technique (Figure 1). All steps through hydrodissection are as usual. I like to make sure that the nuclear surface is exposed, which requires thorough cortical cleanup. I ensure adequate exposure of the phaco tip by sliding the sleeve back.
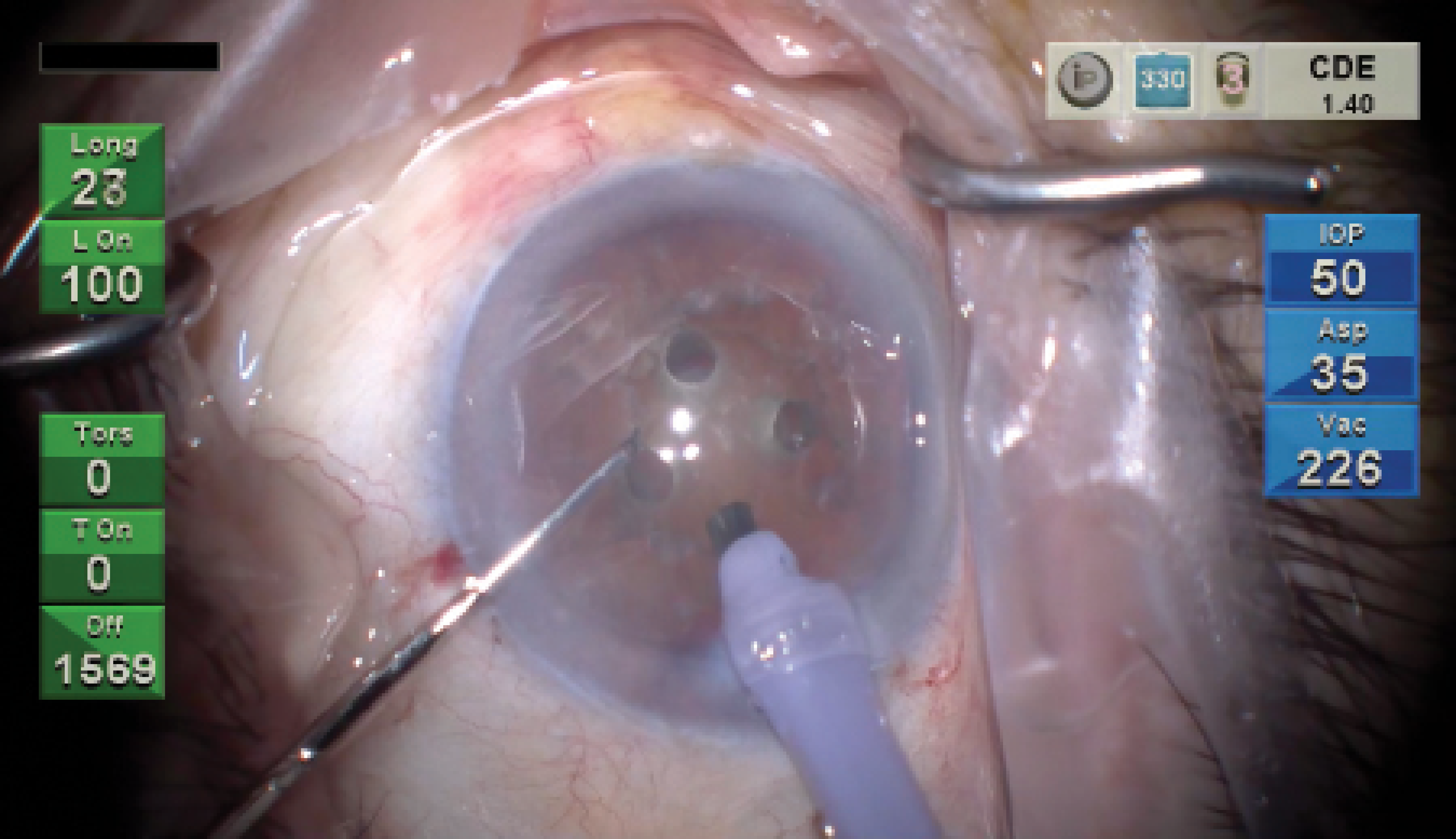
Figure 1. The holes created with the rotary chop technique.
The lens is impaled all the way up to the sleeve of the phaco tip using the phaco chop setting. Footpedal position 1 (irrigation) is then resumed. The phaco tip is removed from the hole, and the lens is rotated 180º away from the surgeon so that the hole is located opposite the wound (Figure 2). Again, the phaco tip is buried in the nucleus up to the phaco sleeve, but this time, vacuum is maintained much as it would be for a normal vertical chop maneuver. The chopper is placed as deeply as possible in the first hole created (Figure 3). Then, the chopper and phaco tip are brought together just as they would be in a vertical chop maneuver.
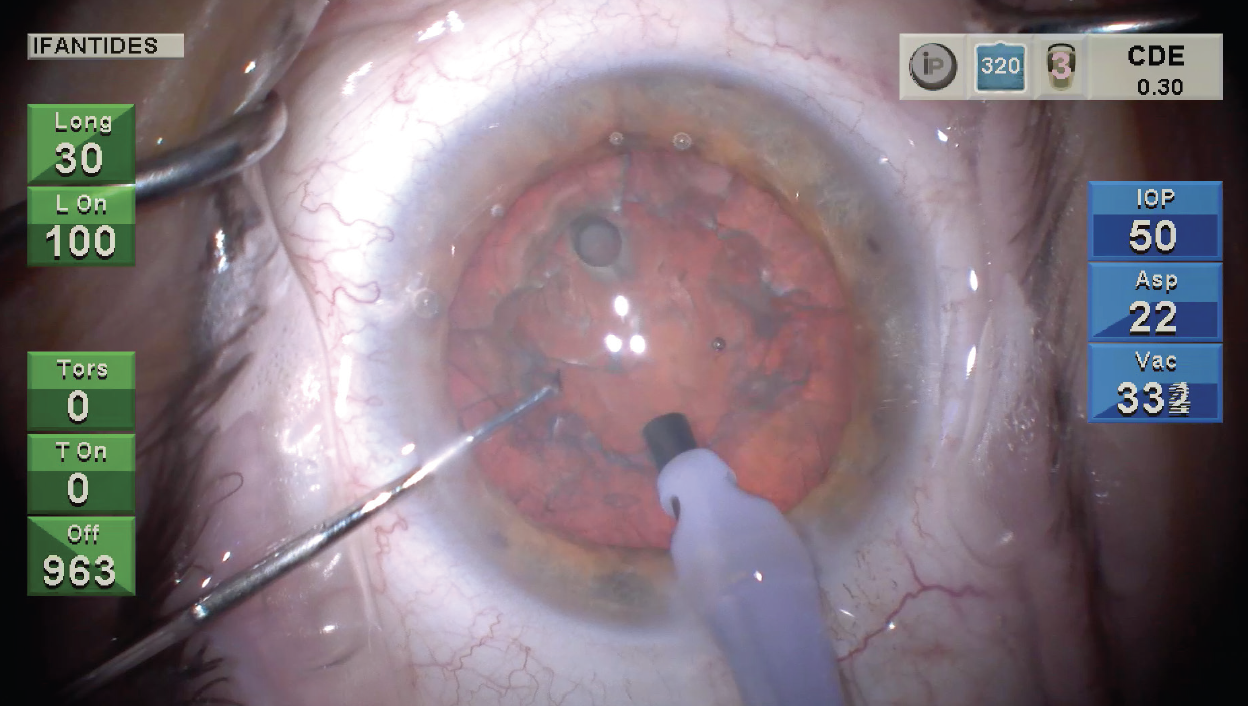
Figure 2. Position 2 of the rotary chop technique. The lens is rotated 180° so that the hole is located opposite the wound.
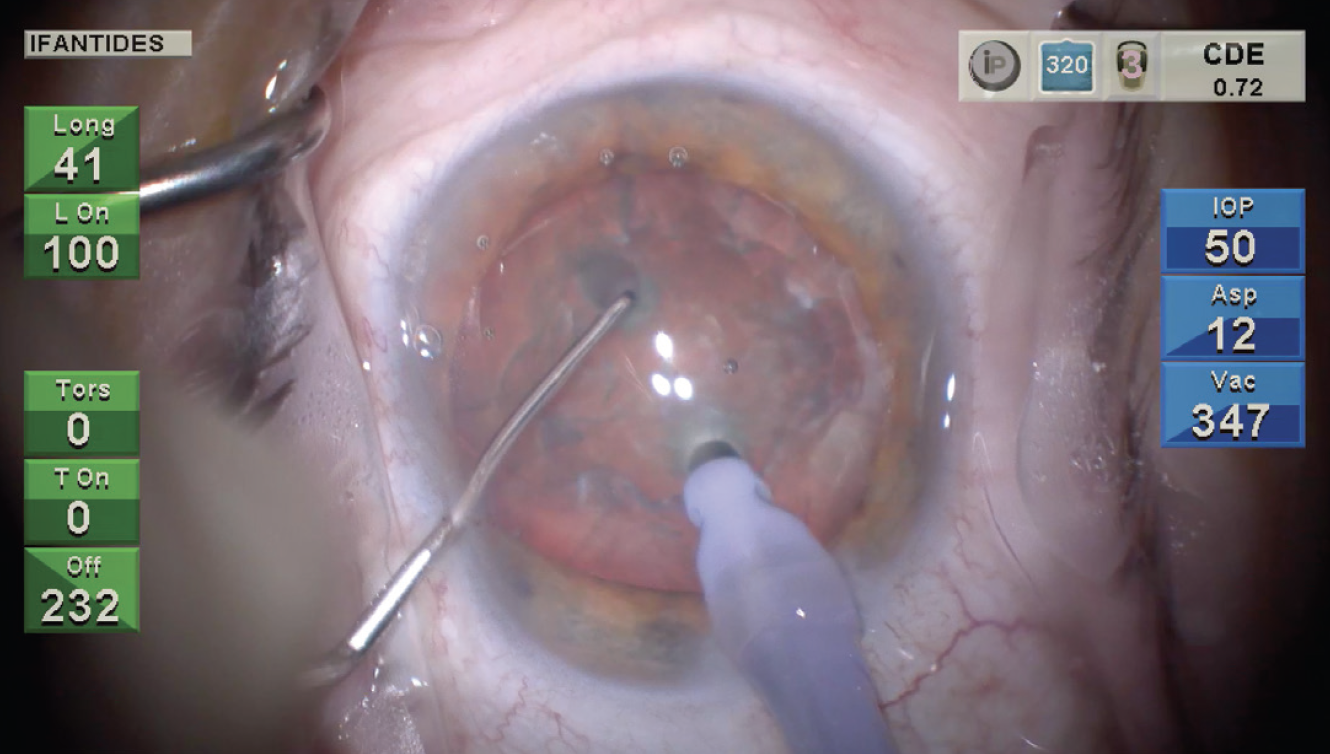
Figure 3. Position 3 of the rotary chop technique with the chopper in the hole.
CONCLUSION
I have successfully taught the rotary chop technique to many trainees. It helps them avoid the common pitfalls of pushing the nucleus off the phaco tip and breaking occlusion during chopping. It has also helped me chop dense lenses while keeping cumulative dissipated energy low.