
The greatest value of topography-guided laser surgery is for treating highly aberrated corneas that are difficult to image with other systems.1,2 The procedure regularizes the corneal surface to improve refractive outcomes. Any change in shape will induce a refractive effect requiring complex and individually derived treatment planning.
Topography-guided laser surgery is effective for improving symptoms (eg, glare, halos, distorted vision), UCVA, and BCVA in eyes with a wide range of irregular astigmatism.3 Indications include complications of previous laser eye surgery,4 asymmetrical astigmatism, corneal scarring after keratoplasty, and—when the procedure is combined with corneal collagen cross-linking (CXL)—ectatic conditions such as post-LASIK ectasia and keratoconus.5 Topography-guided laser systems are also used to treat normal eyes (ie, with good BCVA and low aberrations), although this has not been our practice.6,7
AT A GLANCE
• Topography-guided laser treatment is of most value in eyes with irregular astigmatism that is difficult to treat.
• The procedure may be of considerable help to patients with few other options. It regularizes the corneal surface to improve refractive outcomes.
• The authors developed a topography neutralization technique to compensate for the shape-induced refractive changes.
Several systems are available internationally, but at present, only the Wavelight Allegretto T-CAT (Alcon) and the Navex Quest EC-5000 (Nidek) are approved in the United States (this article includes discussion of off-label indications). We started working with the Wavelight platform in 2003 and more recently began using the Schwind Amaris 1050 SmartSurface (Schwind Eye-Tech Solutions).
METHODS
All topography-guided laser platforms require a linked imaging system from which the treatment is derived and modified by customization. We developed a topography neutralization technique to compensate for the shape-induced refractive changes.8
Surgeons can perform both PRK and LASIK with topography-guided platforms. Using the Wavelight and the Schwind systems, we have performed more than 1,500 cases of transepithelial PRK. Many patients are referred to us for complications of previous refractive surgery that lifting the flap may exacerbate. Low pachymetry readings frequently limit how much further treatment is possible on the residual stromal bed. We administer mitomycin C 0.02% upon the completion of topography-guided PRK (TG-PRK) to minimize haze. We closely monitor patients during the first postoperative week for satisfactory epithelialization, because a delay may cause corneal scarring and increase the risk of herpetic keratitis.
PROCEDURES
Keratoconus
Combining TG-PRK with CXL for the treatment of keratoconus can achieve satisfactory results. We used the Wavelight system to perform the combined procedure on 266 eyes. At 1 year, 133 (50%) had a distance UCVA of 20/40 or better. Seventy eyes (26%) had experienced an improvement in distance BCVA of 2 lines or more, whereas 17 (6%) had lost 2 lines or more. Complications included delayed epithelial healing with subsequent haze that was sufficient in three eyes to reduce BCVA by more than 2 lines, three eyes required corneal transplantation, and two eyes developed herpetic keratitis. In our experience with the Wavelight platform, the treatment axis may be different from the refractive axis after topographic neutralization (Figure 1).
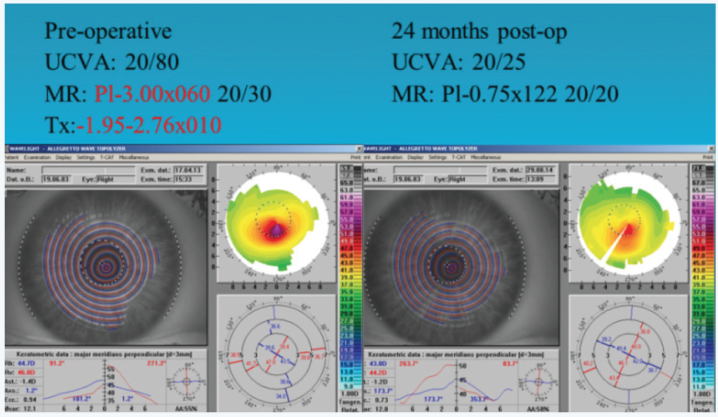
Figure 1. Combined TG-PRK and CXL for keratoconus. Different treatment axis from refractive axis after topographical neutralization.
We have performed the combined procedure using the Schwind system on 133 eyes. One year postoperatively, 71 eyes (63%) had a distance UCVA of 20/40 or better, 29 (22%) had experienced an improvement in distance BCVA of 2 lines or more, and four (3%) had lost 2 lines of distance BCVA.9
Post-LASIK Ectasia
Combining TG-PRK with CXL is an effective treatment for post-LASIK ectasia. Surgery is often possible despite a low pachymetry reading, because treatment is rarely deep enough to reach the flap interface. In our hands, the combined procedure using either laser platform achieved a distance UCVA of 20/40 or better in more than 50% of eyes (n = 29). Distance BCVA improved or did not change in 77% and 91% of eyes treated with the Wavelight and Schwind system, respectively. Our early outcomes show satisfactory safety and efficacy results that are consistent with those achieved by other surgeons using the same or similar techniques (Figure 2).9
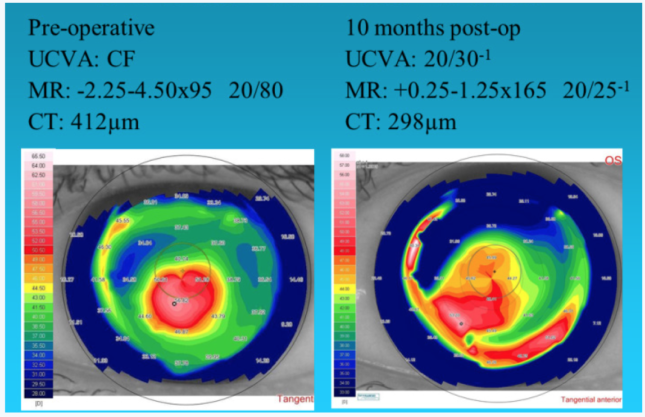
Figure 2. TG-PRK for post-LASIK ectasia.
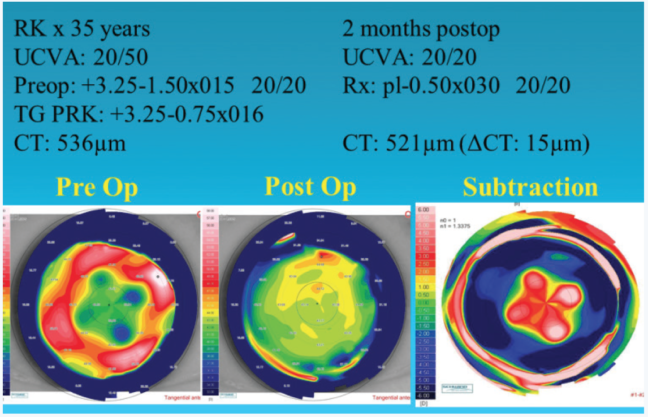
Figure 3. Post-RK TG-PRK.
Complications After Refractive Surgery
TG-PRK is an option for treating eyes with poor distance BCVA and irregular astigmatism after refractive surgery, including radial keratotomy (RK). The procedure can be used to address small optical zones, decentered ablations, corneal scarring, buttonhole flaps, and central islands. We use the approach in symptomatic patients with irregular astigmatism who have sufficient corneal thickness and realistic expectations, provided that image capture is successful.
Of the 12 post-RK patients we treated using the Schwind system, half achieved a distance UCVA of 20/40 or better, and 83% (n = 10) had a distance BCVA that improved or remained unchanged (Figure 3).10 The procedure can also effectively address other causes of severe irregular astigmatism such as LASIK flap trauma (Figure 4).
Postkeratoplasty Astigmatism
TG-PRK has been found effective for the treatment of extreme and/or irregular astigmatism after corneal transplantation (Figure 5). One year after TG-PRK on 38 eyes, 14 (37%) had a distance UCVA better than 20/40, with 12 (32%) gaining 2 or more lines of vision.11
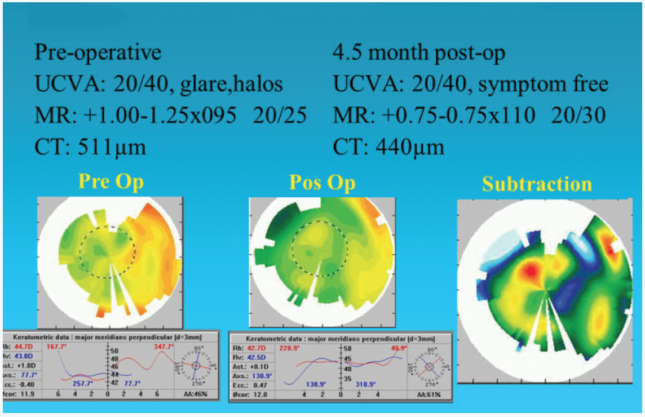
Figure 4. TG-PRK for LASIK flap trauma.
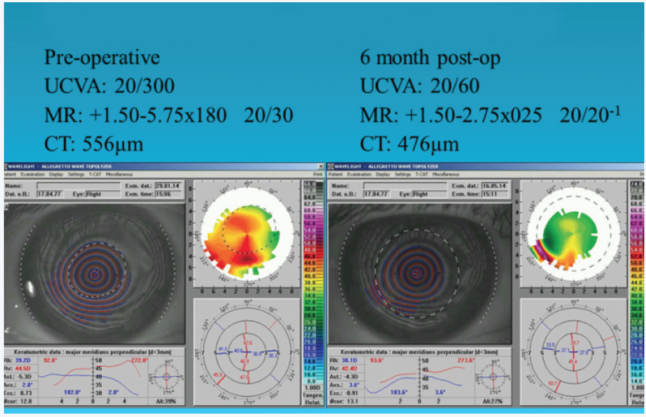
Figure 5. TG-PRK for postkeratoplasty astigmatism.
CONCLUSION
Topography-guided laser surgery may be an effective option for irregular astigmatism in a wide range of conditions that were previously difficult to treat. Longer-term results are needed to establish the procedure’s safety and stability beyond 5 years. In our opinion, treatment planning requires topographical neutralization for the best results, because any shape change will induce a refractive error. Combining TG-PRK with CXL for the treatment of keratoconus and ectasia introduces another variable, but early results have been promising with acceptable safety.
Although surgeons can perform LASIK with a topography-guided laser, we prefer the transepithelial surface approach when possible. Postoperative healing may take longer, but the procedure offers the advantages of tissue sparing and safety in eyes with highly aberrated corneas. TG-PRK may consume more tissue than standard treatments. In our experience, however, the difference is less with the Schwind Amaris 1050 SmartSurface, and there is a limited or filtered option. Newer technology and FDA approval of CXL with the KXL System (Avedro) are widening the scope of treatment.
1. Knorz M, Jendritza B. Topographically-guided laser keratomileusis to treat corneal irregularities. Ophthalmology. 2000;107:1138-1143.
2. Lin DTC, Holland SP, Tan JC, Moloney G. Clinical results of topography-based customized ablations in highly aberrated eyes and keratoconus/ectasia with cross-linking. J Refract Surg. 2012;28:S841-S848.
3. Chen X, Stojanovic A, Zhou W, et al. Transepithelial, topography-guided ablation in the treatment of visual disturbances in LASIK flap or interface complications. J Refract Surg. 2012;28:120-126.
4. Holland S, Lin D, Tan C. Topography-guided laser refractive surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2013;24:302-309.
5. Kanellopoulous A, Binder P. Management of corneal ectasia after LASIK with combined, same-day, topography-guided partial transepithelial PRK and collagen cross-linking: the Athens protocol. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:323-331.
6. Lin DT, Holland SR, Rocha KM, Krueger RR. Method for optimizing topography-guided ablation of highly aberrated eyes with the Allegretto Wave excimer laser. J Refract Surg. 2008;24(4):S439-445.
7. Shetty R, Shroff R. A prospective study to compare visual outcomes between wavefront-optimized and topography- guided ablation profiles in contralateral eyes with myopia. J Refract Surg. 2017;33(1):6-10.
8. Stulting RD, Fant BS; T-CAT Study Group. Results of topography-guided laser in situ keratomileusis custom ablation treatment with a refractive excimer laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2016;42(1):11-18.
9. Holland SP, Lin DTC. Topography-guided ablations: indications and challenges. Presented at Cornea Day ASCRS May 6 2016, New Orleans, LA
10. Termote K, Holland SP, Lin DTC. Early result of topography-guided photorefractive keratectomy for post-LASIK ectasia. Paper presented at: XXXIV Congress of the ESCRS; September 10-14, 2016; Copenhagen, Denmark.
11. Tan JC, Holland SP, Lin DTC, Mosquera SA. Topography guided photorefractive keratectomy for correction of irregular astigmatism after penetrating keratoplasty. Paper presented at: XXXIV Congress of the ESCRS; September 10-14, 2016; Copenhagen, Denmark.




