Why should we ophthalmologists who treat dry eye disease (DED) be interested in intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy, a technology the FDA has cleared for the skin, not specifically for addressing DED?
While some devices treat the downstream consequences of ocular surface disease, IPL sets itself apart by potentially reducing inflammation at the lid margin, thereby addressing the root cause of meibomian gland dysfunction and DED. Both conditions are inflammatory in nature; when we can mediate the inflammation, we can mediate DED.
HOW IT WORKS
IPL has been used in dermatology for decades to treat a variety of skin problems, including facial rosacea. More recently, physicians noted that patients experienced an improvement in symptoms of DED after treatment for facial rosacea.1 Studies show that 80% to 90% of patients with facial rosacea also have ocular rosacea.2 Like DED, rosacea is an inflammatory condition that can be quieted with IPL therapy.
AT A GLANCE
• Meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye disease (DED) are inflammatory in nature.
• Whereas some devices treat the downstream consequences of ocular surface disease, intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy potentially reduces inflammation at the lid margin, thereby addressing the root cause of meibomian gland dysfunction and DED.
• Candidates for IPL include anyone with symptoms of DED who has not responded to traditional therapies, often because of problems with compliance.
• IPL provides a natural transition for practices interested in exploring aesthetic services.
IPL is light filtered to certain wavelengths selected for their absorption by specific target tissues. To treat rosacea, dermatologists target oxyhemoglobin, a component in the walls of telangiectatic vessels. The telangiectasias selectively take up the light, and the heat causes thrombosis, which closes the vessels. To manage DED, ophthalmologists target oxyhemoglobin to treat telangiectasia on the eyelids and lid margins (Figure 1). The mechanism of action is the same: thrombosis of the inflamed blood vessels. Left alone, these leaky vessels may release inflammatory mediators in the eyelids, starting the inflammatory cascade that characterizes DED.
Figure 1. The M22 modular laser, multiapplication platform.
The possibility that there are other concurrent mechanisms of action is being explored. Treatment with IPL may boost upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines and downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines.3,4 In addition to telangiectasias, the light may target pigment in the exoskeleton of Demodex, reducing their number and their possible negative effects related to rosacea.5 IPL may also improve collagen synthesis and boost cellular metabolism by affecting the electron transport chain of mitochondria.6,7
WHO NEEDS IPL?
Candidates for IPL include anyone with symptoms of DED who has not responded to traditional therapies, often because of problems with compliance. This procedure may also be of benefit to patients scheduled for cataract surgery. DED can affect the accuracy of keratometry readings and IOL power calculations, and it can have a negative impact on refractive outcomes. Even when we select the right IOL power and perform surgery perfectly, patients with DED after surgery often complain of discomfort and blurred vision. IPL presents an opportunity to manage DED around cataract surgery without adding drops to the patient’s pre- and postoperative regimen. Knowing that DED treatment will likely improve the outcome of their cataract surgery, patients may be open to an additional procedure that will protect their investment.
Watch It Now
Cynthia Matossian, MD, discusses the intense pulsed light (IPL) procedure, what to expect, who is a candidate, and her experience providing the treatment.
In this episode of CRST Journal Club, Steven Dell, MD, describes the benefits of IPL therapy for the treatment of dry eye disease and meibomian gland dysfunction.
THE TANGIBILITY FACTOR
Patients who see me specifically for DED have typically been experiencing symptoms for some time. They have been going from doctor to doctor and trying artificial tears, prescription eye drops, hygiene practices, and omega-3 fatty acid supplements without success. Some of them have trouble using drops as directed for a variety of reasons. For these frustrated individuals, a device-based therapy may offer an advantage over other treatment options for DED. Compared with many other ocular conditions, DED is ambiguous. There is no clear beginning or end, there is often a disconnect between signs and symptoms, and there is a lack of a gold standard for testing.
When I use devices to test and treat these patients, the tangibility of the hardware imparts tangibility to the disease. In my experience, IPL improves my relationship with patients, because they appreciate that I perform the service. Thus, this form of therapy allows me to address both the biology and the psychology of DED.
IPL IN PRACTICE
IPL is a 10-minute procedure. Patients generally have four treatments separated by 4 weeks. When the patient gets in the chair, I use a metal corneal shield to cover the eyes completely. My IPL device (M22; Lumenis) has tips sized to easily navigate the contours of the eye. The tips are chilled to cool the skin, and according to the manufacturer, its new-generation IPL technology safely ensures delivery of consistent pulses of energy. I gently move the IPL device along the eyelids in a process that is comfortable for patients (Figure 2).
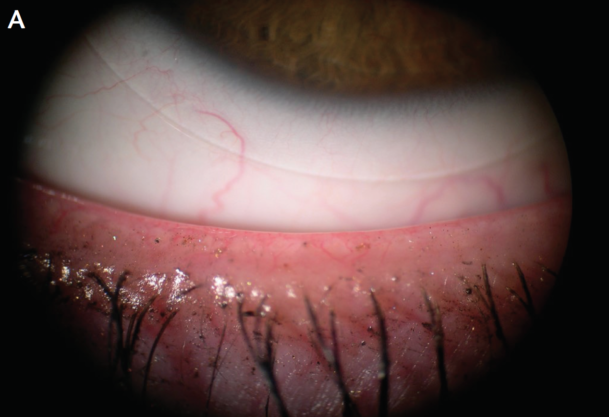
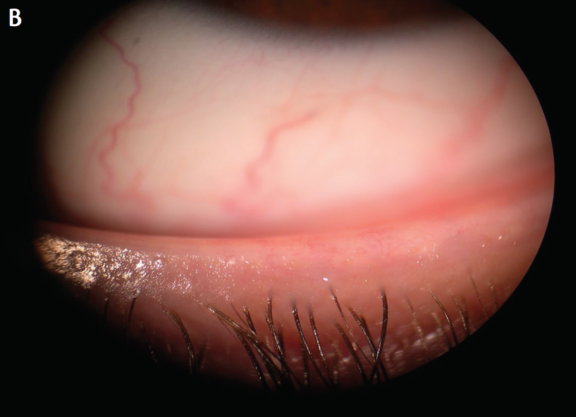
Figure 2. Lid margin at baseline (A) and 4 months after treatment (B).
Multiple studies have established that IPL is safe and effective for the treatment of evaporative DED.1,8 Adverse reactions are uncommon. The metal corneal shield prevents intraocular exposure to the light. Lash loss is possible but rare with careful treatment application. I perform all IPL procedures myself. Patients have no downtime after the procedure, and they need no topical medication or cream. The only restrictions are to avoid direct sun exposure and to use sunscreen. I often treat patients during their lunch breaks.
IPL is not covered by insurance at present. My patients appreciate the option of paying per treatment or purchasing a package, and financing is available.
CONCLUSION
IPL provides a natural transition for practices interested in exploring aesthetic services. The procedure is a welcome addition to the armamentarium for treating ocular surface disease. Its intense light naturally illuminates a pathway toward practice success.
1. Toyos R, McGill W, Briscoe D. Intense pulsed light treatment for dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction: a 3-year retrospective study. Photomed Laser Surg. 2015;33(1):41-46.
2. Viso E, Clemente Millán A, Rodríguez-Ares MT. Rosacea-associated meibomian gland dysfunction – an epidemiological perspective. European Ophthalmic Review. 2014;8(1):13-16.
3. Byun JY, Choi HY, Myung KB, Choi YW. Expression of IL-10, TGF-beta(1) and TNF-alpha in cultured keratinocytes (HaCaT Cells) after IPL treatment or ALA-IPL photodynamic treatment. Ann Dermatol. 2009;21(1):12-17.
4. Lee SY, Park KH, Choi JW, et al. A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blinded, and split-face clinical study on LED phototherapy for skin rejuvenation: clinical, profilometric, histologic, ultrastructural, and biochemical evaluations and comparison of three different treatment settings. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2007;88(1):51-67.
5. Prieto VG, Sadick NS, Lloreta J, et al. Effects of intense pulsed light on sun-damaged human skin, routine, and ultrastructural analysis. Lasers Surg Med. 2002;30(2):82-85.
6. Karu T. Primary and secondary mechanisms of action of visible to near-IR radiation on cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 1999;49(1):1-17.
7. Farivar S, Malekshahabi T, Shiari R. Biological effects of low level laser therapy. J Lasers Med Sci. 2014;5(2):58-62.
8. Gupta PK, Vora GK, Matossian C, et al. Outcomes of intense pulsed light therapy for treatment of evaporative dry eye disease. Can J Ophthalmol. 2016;51(4):249-253.




